Placa ESP32 DEV KIT V1
Informações sobre a placa
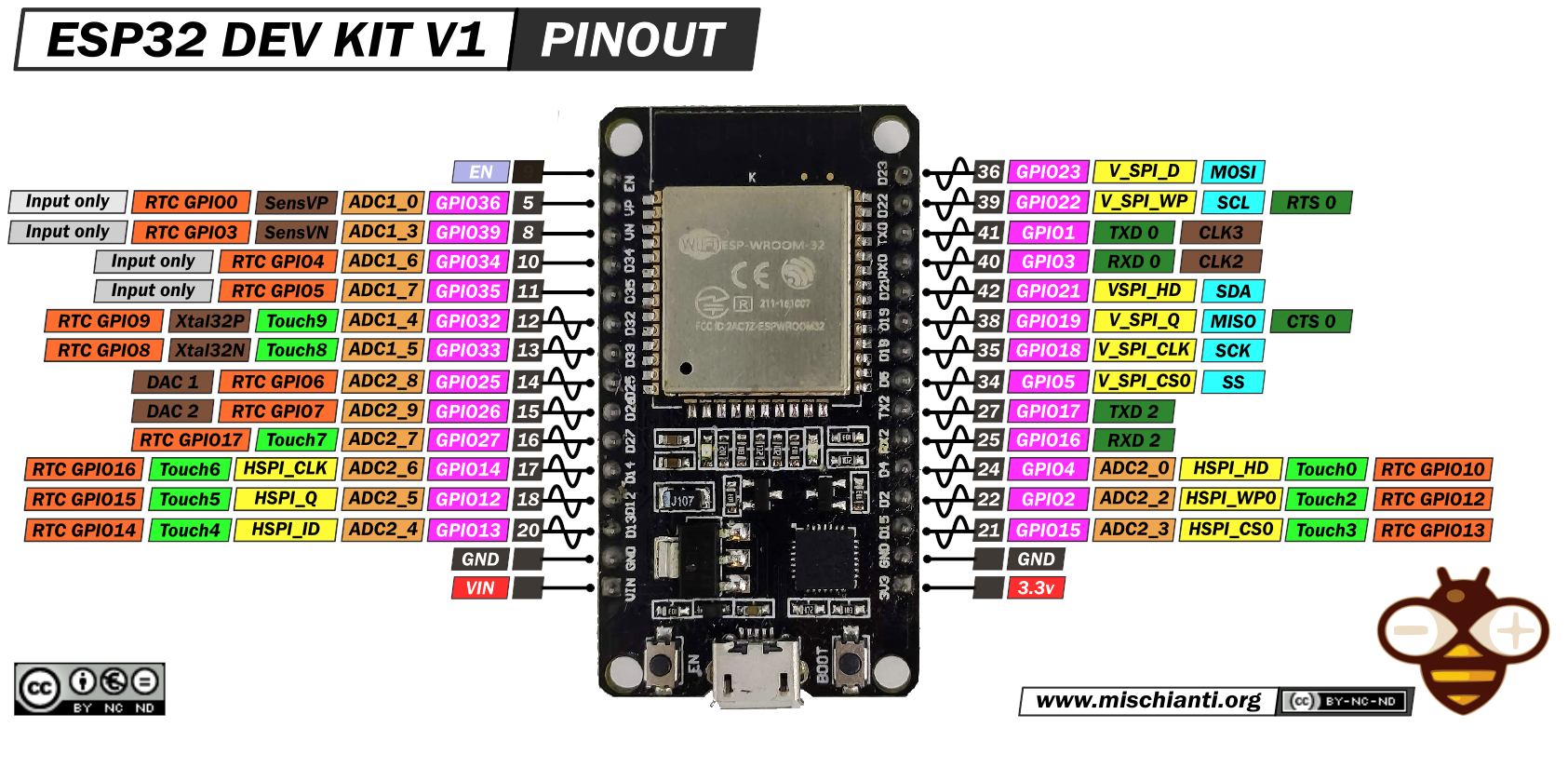
Pinagem: https://mischianti.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/ESP32-DOIT-DEV-KIT-v1-pinout-mischianti.png
Introdução sobre esta placa (ID:2AC7Z) no site do fabricante Espressif ou aqui.
Este fabricante disponibiliza várias versões diferentes de "ESP32":
👉 Esta versão parece ser a "id:2AC7Z-ESPWROOM32": https://fcc.report/FCC-ID/2AC7Z-ESPWROOM32/3212970 (de 2016), também chamada de "ESP-WROVER-KIT" pelo fabricante Espressif, apesar da versão atual (versão 4.1 ser totalmente diferente e contar com leitor de cartões microSD). Mas também não se trata da versão "ESP32-DevKitM-1". Não corresponde à nenhuma placa oficial e atual do fabricante, mas é algo similar à ESP32-DevKitC 🤔.
Segue figura com diagrama de blocos funcional:
Alguma características principais:
- 2 low-power Tensilica 32-bits LX6 (2 cores), clock até 240 MHz, até 600 DMIPS.
- 448 KBytes ROM for boot;
- 530 KBytes on-chip SRAM: data & instructions;
- 8 KBytes SRAM in RTC ("RTC SLOW Memory");
- 8 KBytes SRAM in RTC ("RTC FAST Memory");
- 1 Kbytes EFUSE (256-bits para sistema: MAC address + chip configuration; 768-bits para consumidor).
- Suporta MBytes external QSPI flash SRAM (8 MBytes da SRAM externa mapeados no espaço de dados da CPU, suportando acesso em 8, 16 e 32-bits).
- Consumo máximo (com RF ativo) mA.
- ⚡ Atenção: internamente a placa (e periféricos nela conectados) devem trabalhar à 3,3 Volts ( Volts).
Notamos:
Conversores D/A (bits) nos pinos:
- DAC1: pin D25 ou GPIO25.
- DAC2: pin D26 ou GPIO26.
Conversores A/D (2 12-bits SAR) nos pinos:
Com pré-amplificador (ultra baixo ruído), ganho de até 60 dB (para uso com sensores):
- ADC1_CH0: pin GPIO36 (SENSOR_VP);
- ADC1_CH3: pin GPIO39 (SENSOR_VN).
Sem pré:
- ADC1_outros e ADC2_CH0 ~ ADC2_CH9.
Possui ainda:
- 1 Led 3,3 Volts: mas este led parece que apenas se ativa para indicar que a porta USB está conectada.
- 1 botão de Reset;
- 1 botão de "Enable" ou "Boot".
Mais características introdutórias ver: http://esp32.net
Programação
Guia de programação da Espressif: https://docs.espressif.com/projects/esp-idf/en/latest/esp32/
Software
Ref.: https://docs.espressif.com/projects/esp-idf/en/latest/esp32/get-started/index.html
Para começar a usar o ESP-IDF no ESP32, instale o seguinte software:
- Toolchain (ou Cadeia de ferramentas) para compilar código para ESP32;
- Build tools (ou Ferramentas de construção): CMake e Ninja para criar um aplicativo completo para ESP32;
- ESP-IDF que contém essencialmente API's (bibliotecas de software e código-fonte) para ESP32 e scripts para operar o Toolchain
Instalação
Para instalar todo o software necessário, oferecemos algumas maneiras diferentes de facilitar essa tarefa. Escolha entre uma das opções disponíveis.
IDE
- Plugin Eclipse 👈 Recomendado (melhor, 👍)
Outros:
IDE do Arduíno: Arduino ESP32 (bom apenas para projetos simples) (Atenção: dependendo da conexão, o processo de download de arquivos pode ser demorado - principalmente na UPF ☹️). Considerar o espaço que será ocupado em disco. No caso do MacOS, a pasta:
/Users/fernandopassold/Documents/Arduino/hardware/espressif/esp32/ocupa 7,64 GBytes ⚠️Extensão VSCode (alta curva de aprendizado, trabalha por quantidade exagerada de atalhos por teclas 👎; difícil de ser configurado -- normalmente não se acessa arquivos .json) Informações sobre o "ESP-IDF" VSCode Extesion aqui. Eventualmente será necessário instalar o Tutorial para exemplos na extensão ESP-IDF do VSCode.
Mas este "tutorial" não esclarece muito bem como compilar, transferir e rodar códigos na placa ESP32 usando o VSCode. E a instalação dos exemplos citados acima não pareceu se cumprir. 😠
- Para instalar esta extensão no VSCode recomenda-se o video Getting Started with ESP32 - Step-By-Step Tutorial de Tomasz Tarnowski (menos de 20 minutos) 👌.
O VSCode isoladamente ocupa uns 580 Mbytes + as extensões que ficam armazenadas numa pasta invisível na conta do usuário (
~/.vscode/extension) ; no caso,/Users/fernandopassold/.vscode/extensions/espressif.esp-idf-extension-1.7.1ocupou: 21,5 Mbytes.Obs.: Eventualmente a vantagem do VSCode é a extenção CoPilot que pode facilitar a programação.
Instalação Manual
Para o procedimento manual, compilando e transferindo coódigos para placas ESP32 diretamente do terminal no seiu computador, selecione de acordo com o seu sistema operacional:
Obs.: Falta um "curso" sobre uso de "cmake" para iniciantes... Nada documentado à respeito!
Obs.: No MacOS, a instalação da biblioteca completa para placas ESP32 consumiu 1,89 Gbytes de espaço no disco (na pasta /Users/fernandopassold/esp/esp-idf/) ⚠️.
Mas é criada também outra pasta em ˜/.espressif/ ocupando + 3,05 GBytes ⚠️.
Depois dos pacotes instalados e conectando-se a placa ESP32 no MacOS, aparece:
xxxxxxxxxx~/esp> ls /dev/cu*.* /dev/cu.pci-serial22 /dev/cu.usbserial-0001~/esp> screen /dev/cu.usbserial-0001 115200I (46) boot: Partition Table:I (49) boot: ## Label Usage Type ST Offset LengthI (57) boot: 0 phy_init RF data 01 01 0000f000 00001000I (64) boot: 1 otadata OTA data 01 00 00010000 00002000I (72) boot: 2 nvs WiFi data 01 02 00012000 0000e000I (79) boot: 3 at_customize unknown 40 00 00020000 000e0000I (87) boot: 4 ota_0 OTA app 00 10 00100000 00180000I (94) boot: 5 ota_1 OTA app 00 11 00280000 00180000I (102) boot: End of partition tableE (106) boot: ota data partition invalid and no factory, will try all partitionsI (114) esp_image: segment 0: paddr=0x00100020 vaddr=0x3f400020 size=0x1fdfc (130556) mapI (169) esp_image: segment 1: paddr=0x0011fe24 vaddr=0x3ffc0000 size=0x001ec ( 492) loadI (169) esp_image: segment 2: paddr=0x00120018 vaddr=0x400d0018 size=0xddc74 (908404) mapI (493) esp_image: segment 3: paddr=0x001fdc94 vaddr=0x3ffc01ec size=0x0300c ( 12300) loadI (498) esp_image: segment 4: paddr=0x00200ca8 vaddr=0x40080000 size=0x00400 ( 1024) loadI (500) esp_image: segment 5: paddr=0x002010b0 vaddr=0x40080400 size=0x0eba0 ( 60320) loadI (534) esp_image: segment 6: paddr=0x0020fc58 vaddr=0x400c0000 size=0x00064 ( 100) loadI (543) boot: Loaded app from partition at offset 0x100000I (543) boot: Disabling RNG early entropy source...Bin version(Wrover32):1.1.1I (581) wifi: wifi firmware version: bffcf7fI (581) wifi: config NVS flash: enabledI (581) wifi: config nano formating: disabledI (591) wifi: Init dynamic tx buffer num: 32I (591) wifi: Init data frame dynamic rx buffer num: 32I (591) wifi: Init management frame dynamic rx buffer num: 32I (597) wifi: wifi driver task: 3ffdf604, prio:23, stack:4096I (602) wifi: Init static rx buffer num: 10I (606) wifi: Init dynamic rx buffer num: 32I (610) wifi: wifi power manager task: 0x3ffe3ce4 prio: 21 stack: 2560I (642) wifi: mode : sta (48:e7:29:b6:cd:b4)I (645) wifi: mode : sta (48:e7:29:b6:cd:b4) + softAP (48:e7:29:b6:cd:b5)I (652) wifi: mode : sta (48:e7:29:b6:cd:b4)Obs.: para sair do "screen" aperte a combinação de teclas: CTRL-A+ K.
Eventualmente será necessário pressionar o botão "EN" ou "BOOT" na placa para que seja estabelecida a comunicação com a placa ESP32.
👋 E antes de tentar programar a placa usando o Terminal, não esquecer de dar o comando:
. $HOME/esp/esp-idf/export.shse estiver usando bash ou zsh;. $HOME/esp/esp-idf/export.fishse estiver usando o fish.
Atenção: o arquivo export.sh não deve ser do tipo executável.
Este comando atualiza o
$PATHde seu sistema. No caso do MacOS, por exemplo:xxxxxxxxxx(base) fernandopassold@MacBook-Pro-de-Fernando ~ % echo $PATH/opt/anaconda3/bin:/opt/anaconda3/condabin:/usr/local/bin:/System/Cryptexes/App/usr/bin:/usr/bin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/sbin:/Applications/VMware Fusion.app/Contents/Public:/Library/TeX/texbin:/var/run/com.apple.security.cryptexd/codex.system/bootstrap/usr/local/bin:/var/run/com.apple.security.cryptexd/codex.system/bootstrap/usr/bin:/var/run/com.apple.security.cryptexd/codex.system/bootstrap/usr/appleinternal/bin(base) fernandopassold@MacBook-Pro-de-Fernando ~ % pwd
Este comando executa algumas tarefas. Por exemplo:
xfernandopassold@MacBook-Pro-de-Fernando ~/e/esp-idf (master)> . $HOME/esp/esp-idf/export.fish (base) Setting IDF_PATH to '/Users/fernandopassold/esp/esp-idf'Detecting the Python interpreterChecking "python3" ...Python 3.11.7python3 has been detectedChecking Python compatibilityChecking other ESP-IDF version.Adding ESP-IDF tools to PATH...Checking if Python packages are up to date...Constraint file: /Users/fernandopassold/.espressif/espidf.constraints.v5.4.txtRequirement files: - /Users/fernandopassold/esp/esp-idf/tools/requirements/requirements.core.txtPython being checked: /Users/fernandopassold/.espressif/python_env/idf5.4_py3.11_env/bin/pythonPython requirements are satisfied.Added the following directories to PATH:/Users/fernandopassold/esp/esp-idf/components/espcoredump/Users/fernandopassold/esp/esp-idf/components/partition_table/Users/fernandopassold/esp/esp-idf/components/app_update/Users/fernandopassold/.espressif/tools/xtensa-esp-elf-gdb/14.2_20240403/xtensa-esp-elf-gdb/bin/Users/fernandopassold/.espressif/tools/riscv32-esp-elf-gdb/14.2_20240403/riscv32-esp-elf-gdb/bin/Users/fernandopassold/.espressif/tools/xtensa-esp-elf/esp-13.2.0_20240305/xtensa-esp-elf/bin/Users/fernandopassold/.espressif/tools/riscv32-esp-elf/esp-13.2.0_20240305/riscv32-esp-elf/bin/Users/fernandopassold/.espressif/tools/esp32ulp-elf/2.38_20240113/esp32ulp-elf/bin/Users/fernandopassold/.espressif/tools/openocd-esp32/v0.12.0-esp32-20240318/openocd-esp32/bin/Users/fernandopassold/.espressif/tools/xtensa-esp-elf-gdb/14.2_20240403/xtensa-esp-elf-gdb/bin/Users/fernandopassold/.espressif/tools/riscv32-esp-elf-gdb/14.2_20240403/riscv32-esp-elf-gdb/bin/Users/fernandopassold/.espressif/tools/xtensa-esp-elf/esp-13.2.0_20240305/xtensa-esp-elf/bin/Users/fernandopassold/.espressif/tools/riscv32-esp-elf/esp-13.2.0_20240305/riscv32-esp-elf/bin/Users/fernandopassold/.espressif/tools/esp32ulp-elf/2.38_20240113/esp32ulp-elf/bin/Users/fernandopassold/.espressif/tools/openocd-esp32/v0.12.0-esp32-20240318/openocd-esp32/bin/Users/fernandopassold/.espressif/python_env/idf5.4_py3.11_env/bin/Users/fernandopassold/esp/esp-idf/toolsDone! You can now compile ESP-IDF projects.Go to the project directory and run: idf.py buildfernandopassold@MacBook-Pro-de-Fernando ~/e/esp-idf (master)> idf.py --version (base) ESP-IDF v5.4-dev-610-g003f3bb5dcfernandopassold@MacBook-Pro-de-Fernando ~/e/esp-idf (master)>
Atenção: usuários Windows (e Linux), provavelmente será necessário instalar o PuTTY SSH Client para estabelecer a comunicação com a placa. E depois será necessário configurar a comunicação serial para:
- Speed (baud): 115200;
- Data bits: 8;
- Stop bits: 1;
- Parity: None;
- Row control: XON/XOFF.
✏️ Primeiro Projeto
Se você já tiver o ESP-IDF instalado e não estiver usando uma IDE, poderá criar seu primeiro projeto a partir da linha de comando após Iniciar um Projeto no Windows ou Iniciar um Projeto no Linux e macOS.
1. Iniciando trabalhos com placas ESP32
xxxxxxxxxx$ cd ~/esp/esp-idf # chaveia até pasta com arquivos fonte para compilações, etc...$ . $HOME/esp/esp-idf/export.sh # realizando o "source" para diretórios necessáriosObs.: o último comando acima, deve ser excecutado nesta forma, incluindo o ".". Note: o arquivo export.sh não deveria ser um arquivo executável, por isto é acionado desta forma.
2. Iniciando o projeto
xxxxxxxxxx$ cd ~/esp$ cp -r $IDF_PATH/examples/get-started/hello_world . # copia projeto hello_world da EspressifObs.: não esqueça o "." final no comando acima, senão não será criada uma nova pasta chamada hello_world.
Um novo diretório ~/esp/hello_world deve ter sido criado contendo uma estrutura contendo pastas como:
xxxxxxxxxx.├── CMakeLists.txt├── README.md├── build│ ├── CMakeCache.txt| :├── main│ ├── CMakeLists.txt│ └── hello_world_main.c├── pytest_hello_world.py├── sdkconfig└── sdkconfig.ci613 directories, 1317 filesO código que se deseja compilar é o ~/esp/hello_world/main/hello_world_man.c que contêm algo como:
xxxxxxxxxx/* * SPDX-FileCopyrightText: 2010-2022 Espressif Systems (Shanghai) CO LTD * * SPDX-License-Identifier: CC0-1.0 */void app_main(void){ printf("Hello world!\n"); /* Print chip information */ esp_chip_info_t chip_info; uint32_t flash_size; esp_chip_info(&chip_info); printf("This is %s chip with %d CPU core(s), %s%s%s%s, ", CONFIG_IDF_TARGET, chip_info.cores, (chip_info.features & CHIP_FEATURE_WIFI_BGN) ? "WiFi/" : "", (chip_info.features & CHIP_FEATURE_BT) ? "BT" : "", (chip_info.features & CHIP_FEATURE_BLE) ? "BLE" : "", (chip_info.features & CHIP_FEATURE_IEEE802154) ? ", 802.15.4 (Zigbee/Thread)" : ""); unsigned major_rev = chip_info.revision / 100; unsigned minor_rev = chip_info.revision % 100; printf("silicon revision v%d.%d, ", major_rev, minor_rev); if(esp_flash_get_size(NULL, &flash_size) != ESP_OK) { printf("Get flash size failed"); return; } printf("%" PRIu32 "MB %s flash\n", flash_size / (uint32_t)(1024 * 1024), (chip_info.features & CHIP_FEATURE_EMB_FLASH) ? "embedded" : "external"); printf("Minimum free heap size: %" PRIu32 " bytes\n", esp_get_minimum_free_heap_size()); for (int i = 10; i >= 0; i--) { printf("Restarting in %d seconds...\n", i); vTaskDelay(1000 / portTICK_PERIOD_MS); } printf("Restarting now.\n"); fflush(stdout); esp_restart();}Obs.; Note que este código exemplo já implementa uma task usando a biblioteca do FreeRTOS.
3. Configurando placa com projeto
Associa placa com o projeto:
xxxxxxxxxx$ cd ~/esp/hello_world$ idf.py set-target esp32$ idf.py menuconfig # Este comando pode ser suprimido!Este último permite configurar vários detalhes especiais mais específicos (não altere nada se não souber o que alterar). Mas permite configurar o SSID da sua rede WiFi, incluindo a senha. Neste caso, na janela inicial que se abre selecionar "Componet config":
xxxxxxxxxx(Top) Espressif IoT Development Framework Configuration Build type ---> Bootloader config ---> Security features ---> Application manager ---> Serial flasher config ---> Partition Table ---> Compiler options ---> Component config --->[ ] Make experimental features visible[Space/Enter] Toggle/enter [ESC] Leave menu [S] Save[O] Load [?] Symbol info [/] Jump to symbol[F] Toggle show-help mode [C] Toggle show-name mode [A] Toggle show-all mode[Q] Quit (prompts for save) [D] Save minimal config (advanced)Selecione "Component config" e devem aparecer uma longa lista de novas opções:
xxxxxxxxxx(Top) → Component config ↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑Espressif IoT Development Framework Configuration Partition API Configuration ---- PHY ---> Power Management ---> ESP PSRAM ---> ESP Ringbuf ---> ESP System Settings ---> IPC (Inter-Processor Call) ---> ESP Timer (High Resolution Timer) ---> Wi-Fi ---> Core dump ---> FAT Filesystem support ---> FreeRTOS ---> Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL) and Low Level (LL) ---> Heap memory debugging ---> Log ---> LWIP ---> ↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓[Space/Enter] Toggle/enter [ESC] Leave menu [S] Save[O] Load [?] Symbol info [/] Jump to symbol[F] Toggle show-help mode [C] Toggle show-name mode [A] Toggle show-all mode[Q] Quit (prompts for save) [D] Save minimal config (advanced)🤦♂️ Ops.... A Espressif não mostra como configurar o SSID e senha do seu WiFi... 😞
Mas note que podemos configurar detalhes da biblioteca FreeRTOS. Abaixo aparecem as opções para: FreeRTOS → Kernel):
xxxxxxxxxx(Top) → Component config → FreeRTOS → Kernel Espressif IoT Development Framework Configuration[ ] Run the Amazon SMP FreeRTOS kernel instead (FEATURE UNDER DEVELOPMENT)[ ] Run FreeRTOS only on first core(100) configTICK_RATE_HZ configCHECK_FOR_STACK_OVERFLOW (Check using canary bytes (Method 2)) --->(1) configNUM_THREAD_LOCAL_STORAGE_POINTERS(1536) configMINIMAL_STACK_SIZE (Idle task stack size)[ ] configUSE_IDLE_HOOK[ ] configUSE_TICK_HOOK(16) configMAX_TASK_NAME_LEN[ ] configENABLE_BACKWARD_COMPATIBILITY(Tmr Svc) configTIMER_SERVICE_TASK_NAME configTIMER_SERVICE_TASK_CORE_AFFINITY (No affinity) --->(1) configTIMER_TASK_PRIORITY(2048) configTIMER_TASK_STACK_DEPTH(10) configTIMER_QUEUE_LENGTH(0) configQUEUE_REGISTRY_SIZE(1) configTASK_NOTIFICATION_ARRAY_ENTRIES[ ] configUSE_TRACE_FACILITY[ ] configUSE_LIST_DATA_INTEGRITY_CHECK_BYTES[ ] configGENERATE_RUN_TIME_STATS[ ] configUSE_APPLICATION_TASK_TAG[Space/Enter] Toggle/enter [ESC] Leave menu [S] Save[O] Load [?] Symbol info [/] Jump to symbol[F] Toggle show-help mode [C] Toggle show-name mode [A] Toggle show-all mode[Q] Quit (prompts for save) [D] Save minimal config (advanced)e as opções para: FreeRTOS → Port:
xxxxxxxxxx(Top) → Component config → FreeRTOS → Port Espressif IoT Development Framework Configuration[*] Wrap task functions[ ] Enable stack overflow debug watchpoint[*] Enable thread local storage pointers deletion callbacks[ ] Enable task pre-deletion hook[ ] Enable static task clean up hook (DEPRECATED)[*] Check that mutex semaphore is given by owner task(1536) ISR stack size[*] Enable backtrace from interrupt to task context[ ] Use float in Level 1 ISR Tick timer source (Xtensa Only) (Timer 0 (int 6, level 1)) --->[ ] Place FreeRTOS functions into Flash[ ] Tests compliance with Vanilla FreeRTOS port*_CRITICAL calls[Space/Enter] Toggle/enter [ESC] Leave menu [S] Save[O] Load [?] Symbol info [/] Jump to symbol[F] Toggle show-help mode [C] Toggle show-name mode [A] Toggle show-all mode[Q] Quit (prompts for save) [D] Save minimal config (advanced)Atenção: se não souber o que configurar de maneira diferente do default recomenda-se não alterar nenhuma opção.
4. Compilando
xxxxxxxxxx$ idf.py buildObs.: este comando pode levar um certo tempo para terminar de ser exceutado. Neste caso, a primeira vez em que foi compilado, exigiu 1 min 35 segundos:
xxxxxxxxxx% START_TIME=$SECONDS% idf.py build...Partition table binary generated. Contents:*******************************************************************************# ESP-IDF Partition Table# Name, Type, SubType, Offset, Size, Flagsnvs,data,nvs,0x9000,24K,phy_init,data,phy,0xf000,4K,factory,app,factory,0x10000,1M,*******************************************************************************...-- Configuring done (13.9s)-- Generating done (0.2s)-- Build files have been written to: /Users/fernandopassold/esp/hello_world/build/bootloader...[107/108] Generating binary image from built executableesptool.py v4.8.dev3Creating esp32 image...Merged 2 ELF sectionsSuccessfully created esp32 image.Generated /Users/fernandopassold/esp/hello_world/build/bootloader/bootloader.bin[108/108] cd /Users/fernandopassold/esp/hello_world/build/bootl...fernandopassold/esp/hello_world/build/bootloader/bootloader.binBootloader binary size 0x6880 bytes. 0x780 bytes (7%) free.[971/972] Generating binary image from built executableesptool.py v4.8.dev3Creating esp32 image...Merged 2 ELF sectionsSuccessfully created esp32 image.Generated /Users/fernandopassold/esp/hello_world/build/hello_world.bin[972/972] cd /Users/fernandopassold/esp/hello_world/build/esp-i...in /Users/fernandopassold/esp/hello_world/build/hello_world.binhello_world.bin binary size 0x2b0f0 bytes. Smallest app partition is 0x100000 bytes. 0xd4f10 bytes (83%) free.Project build complete. To flash, run: idf.py flashor idf.py -p PORT flashor python -m esptool --chip esp32 -b 460800 --before default_reset --after hard_reset write_flash --flash_mode dio --flash_size 2MB --flash_freq 40m 0x1000 build/bootloader/bootloader.bin 0x8000 build/partition_table/partition-table.bin 0x10000 build/hello_world.binor from the "/Users/fernandopassold/esp/hello_world/build" directory python -m esptool --chip esp32 -b 460800 --before default_reset --after hard_reset write_flash "@flash_args"% ELAPSED_TIME=$(($SECONDS - $START_TIME))% echo "$(($ELAPSED_TIME/60)) min $(($ELAPSED_TIME%60)) sec" 1 min 35 sec
5. Transferindo código (compilado) para a placa
xxxxxxxxxx$ idf.py -p PORT flashonde <PORT> deve ser o "caminho" que indica a conexão/porta serial do seu computador com a placa ESP32. Você pode seguir as dicas passadas pela Espressif em: Establish Serial Connection with ESP32.
No caso do Windows ficaria algo como:
xxxxxxxxxxidf.py -p COM3 -b 115200 flashNeste caso:
xxxxxxxxxx% ls /dev/cu.* # buscando a placa/dev/cu.SLAB_USBtoUART /dev/cu.pci-serial22 /dev/cu.usbserial-0001% # placa no MacOS, normalmente: /dev/cu.usbserial-1401, neste caso: /dev/cu.usbserial-0001% idf.py -p /dev/cu.usbserial-0001 -b 115200 flashEsta transferência é rápida. Neste casou durou apenas uns 25 segundos.
Obs. por padrão, o baud rate de placas RESP32 é de 115200 bps.
6. Monitorando a saída serial (saída do programa)
xxxxxxxxxx$ idf.py -p <PORT> monitorAntes: de executar o comando acima, a própria Espressif recomenda, na placa ESP32, pressionar o botão "BOOT" (para forçar carga da nova versão do firmware) e depois "EN" (para resetar a placa).
Obs.: Em máquinas Windows, será necessário instalar o PuTTY SSH Client. E depois configurar a comunicação serial para:
- Speed (baud): 115200;
- Data bits: 8;
- Stop bits: 1;
- Parity: None;
- Row control: XON/XOFF.
Se tudo estiver correto, devem ter surgido as seguintes informações na tela do monitor serial:
xxxxxxxxxxHello world!This is esp32 chip with 2 CPU core(s), WiFi/BTBLE, silicon revision v3.1, 2MB external flashMinimum free heap size: 305360 bytesRestarting in 10 seconds...Restarting in 9 seconds...Restarting in 8 seconds...Restarting in 7 seconds...Restarting in 6 seconds...Restarting in 5 seconds...Restarting in 4 seconds...Restarting in 3 seconds...Restarting in 2 seconds...Restarting in 1 seconds...Restarting in 0 seconds...Restarting now.ets Jul 29 2019 12:21:46Note que esta aplicação teste fica repetidamente exibindo a mensagem "Hello world!" e rebootando o dispositivo à cada 10 segundos.
Para interromper a monitoramento, pressionar a combinação de teclas CTRL+].
Neste caso específico, na janela de terminal apareceu algo como:
xxxxxxxxxx% idf.py -p /dev/cu.usbserial-0001 monitorExecuting action: monitorRunning idf_monitor in directory /Users/fernandopassold/esp/hello_worldExecuting "/Users/fernandopassold/.espressif/python_env/idf5.4_py3.11_env/bin/python /Users/fernandopassold/esp/esp-idf/tools/idf_monitor.py -p /dev/cu.usbserial-0001 -b 115200 --toolchain-prefix xtensa-esp32-elf- --target esp32 --revision 0 /Users/fernandopassold/esp/hello_world/build/hello_world.elf -m '/Users/fernandopassold/.espressif/python_env/idf5.4_py3.11_env/bin/python' '/Users/fernandopassold/esp/esp-idf/tools/idf.py' '-p' '/dev/cu.usbserial-0001'"...--- esp-idf-monitor 1.4.0 on /dev/cu.usbserial-0001 115200 ------ Quit: Ctrl+] | Menu: Ctrl+T | Help: Ctrl+T followed by Ctrl+H ---p����� �� � ��p...� �pets Jul 29 2019 12:21:46rst:0x1 (POWERON_RESET),boot:0x13 (SPI_FAST_FLASH_BOOT)configsip: 0, SPIWP:0xeeclk_drv:0x00,q_drv:0x00,d_drv:0x00,cs0_drv:0x00,hd_drv:0x00,wp_drv:0x00mode:DIO, clock div:2load:0x3fff0030,len:7176load:0x40078000,len:15564ho 0 tail 12 room 4load:0x40080400,len:40x40080400: _init at ??:?load:0x40080404,len:3904entry 0x40080640I (31) boot: ESP-IDF v5.4-dev-610-g003f3bb5dc-dirty 2nd stage bootloaderI (31) boot: compile time Jun 5 2024 17:15:50I (33) boot: Multicore bootloaderI (37) boot: chip revision: v3.1I (41) boot.esp32: SPI Speed : 40MHzI (46) boot.esp32: SPI Mode : DIOI (50) boot.esp32: SPI Flash Size : 2MBI (55) boot: Enabling RNG early entropy source...I (60) boot: Partition Table:I (64) boot: ## Label Usage Type ST Offset LengthI (71) boot: 0 nvs WiFi data 01 02 00009000 00006000I (79) boot: 1 phy_init RF data 01 01 0000f000 00001000I (86) boot: 2 factory factory app 00 00 00010000 00100000I (94) boot: End of partition tableI (98) esp_image: segment 0: paddr=00010020 vaddr=3f400020 size=093d0h ( 37840) mapI (119) esp_image: segment 1: paddr=000193f8 vaddr=3ffb0000 size=02200h ( 8704) loadI (123) esp_image: segment 2: paddr=0001b600 vaddr=40080000 size=04a18h ( 18968) loadI (133) esp_image: segment 3: paddr=00020020 vaddr=400d0020 size=138c8h ( 80072) mapI (161) esp_image: segment 4: paddr=000338f0 vaddr=40084a18 size=077dch ( 30684) loadI (180) boot: Loaded app from partition at offset 0x10000I (180) boot: Disabling RNG early entropy source...I (192) cpu_start: Multicore appI (200) cpu_start: Pro cpu start user codeI (200) cpu_start: cpu freq: 160000000 HzI (200) app_init: Application information:I (203) app_init: Project name: hello_worldI (208) app_init: App version: 1I (213) app_init: Compile time: Jun 5 2024 17:15:23I (219) app_init: ELF file SHA256: c42f6053b...I (224) app_init: ESP-IDF: v5.4-dev-610-g003f3bb5dc-dirtyI (231) efuse_init: Min chip rev: v0.0I (236) efuse_init: Max chip rev: v3.99 I (241) efuse_init: Chip rev: v3.1I (246) heap_init: Initializing. RAM available for dynamic allocation:I (253) heap_init: At 3FFAE6E0 len 00001920 (6 KiB): DRAMI (259) heap_init: At 3FFB2AC8 len 0002D538 (181 KiB): DRAMI (265) heap_init: At 3FFE0440 len 00003AE0 (14 KiB): D/IRAMI (271) heap_init: At 3FFE4350 len 0001BCB0 (111 KiB): D/IRAMI (278) heap_init: At 4008C1F4 len 00013E0C (79 KiB): IRAMI (285) spi_flash: detected chip: genericI (288) spi_flash: flash io: dioW (292) spi_flash: Detected size(4096k) larger than the size in the binary image header(2048k). Using the size in the binary image header.I (306) main_task: Started on CPU0I (316) main_task: Calling app_main()Hello world!This is esp32 chip with 2 CPU core(s), WiFi/BTBLE, silicon revision v3.1, 2MB external flashMinimum free heap size: 305360 bytesRestarting in 10 seconds...Restarting in 9 seconds...Restarting in 8 seconds...Restarting in 7 seconds...Restarting in 6 seconds...Restarting in 5 seconds...Restarting in 4 seconds...Restarting in 3 seconds...Restarting in 2 seconds...Restarting in 1 seconds...Restarting in 0 seconds...Restarting now.ets Jul 29 2019 12:21:46rst:0xc (SW_CPU_RESET),boot:0x13 (SPI_FAST_FLASH_BOOT)configsip: 0, SPIWP:0xeeclk_drv:0x00,q_drv:0x00,d_drv:0x00,cs0_drv:0x00,hd_drv:0x00,wp_drv:0x00mode:DIO, clock div:2load:0x3fff0030,len:7176load:0x40078000,len:15564ho 0 tail 12 room 4load:0x40080400,len:40x40080400: _init at ??:?load:0x40080404,len:3904entry 0x40080640I (31) boot: ESP-IDF v5.4-dev-610-g003f3bb5dc-dirty 2nd stage bootloaderI (31) boot: compile time Jun 5 2024 17:15:50I (33) boot: Multicore bootloaderI (37) boot: chip revision: v3.1I (41) boot.esp32: SPI Speed : 40MHzI (46) boot.esp32: SPI Mode : DIOI (50) boot.esp32: SPI Flash Size : 2MBI (55) boot: Enabling RNG early entropy source...I (60) boot: Partition Table:I (64) boot: ## Label Usage Type ST Offset LengthI (71) boot: 0 nvs WiFi data 01 02 00009000 00006000I (79) boot: 1 phy_init RF data 01 01 0000f000 00001000I (86) boot: 2 factory factory app 00 00 00010000 00100000I (94) boot: End of partition tableI (98) esp_image: segment 0: paddr=00010020 vaddr=3f400020 size=093d0h ( 37840) mapI (119) esp_image: segment 1: paddr=000193f8 vaddr=3ffb0000 size=02200h ( 8704) loadI (123) esp_image: segment 2: paddr=0001b600 vaddr=40080000 size=04a18h ( 18968) loadI (133) esp_image: segment 3: paddr=00020020 vaddr=400d0020 size=138c8h ( 80072) mapI (161) esp_image: segment 4: paddr=000338f0 vaddr=40084a18 size=077dch ( 30684) loadI (180) boot: Loaded app from partition at offset 0x10000I (180) boot: Disabling RNG early entropy source...I (191) cpu_start: Multicore appI (200) cpu_start: Pro cpu start user codeI (200) cpu_start: cpu freq: 160000000 HzI (200) app_init: Application information:I (203) app_init: Project name: hello_worldI (208) app_init: App version: 1I (213) app_init: Compile time: Jun 5 2024 17:15:23I (219) app_init: ELF file SHA256: c42f6053b...I (224) app_init: ESP-IDF: v5.4-dev-610-g003f3bb5dc-dirtyI (231) efuse_init: Min chip rev: v0.0I (235) efuse_init: Max chip rev: v3.99 I (240) efuse_init: Chip rev: v3.1I (246) heap_init: Initializing. RAM available for dynamic allocation:I (253) heap_init: At 3FFAE6E0 len 00001920 (6 KiB): DRAMI (259) heap_init: At 3FFB2AC8 len 0002D538 (181 KiB): DRAMI (265) heap_init: At 3FFE0440 len 00003AE0 (14 KiB): D/IRAMI (271) heap_init: At 3FFE4350 len 0001BCB0 (111 KiB): D/IRAMI (278) heap_init: At 4008C1F4 len 00013E0C (79 KiB): IRAMI (285) spi_flash: detected chip: genericI (288) spi_flash: flash io: dioW (292) spi_flash: Detected size(4096k) larger than the size in the binary image header(2048k). Using the size in the binary image header.I (306) main_task: Started on CPU0I (316) main_task: Calling app_main()Hello world!This is esp32 chip with 2 CPU core(s), WiFi/BTBLE, silicon revision v3.1, 2MB external flashMinimum free heap size: 305360 bytesRestarting in 10 seconds...Restarting in 9 seconds...Restarting in 8 seconds...Restarting in 7 seconds...Restarting in 6 seconds...(base) fernandopassold@MacBook-Pro-de-Fernando hello_world % Mais Info
Mais info sobre compilar este projeto (no Terminal!) ver [aqui].