Exemplo de Projeto de Lead usando Contribuição angular.
Aula de 09.06.2021
Uso do script angulos3.m arc.m.
Exemplo: Projete um compensadores por avanço de fase que reduza por 2 enquanto mantêm sobressinal abaixo de 30% (baseado no example 9.4 de NISE):
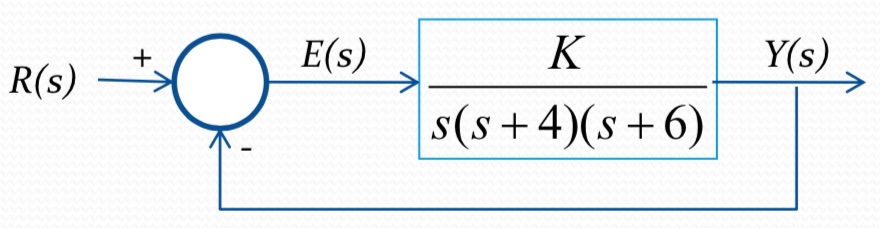
Sintonizando um controlador proporcional para este sistema de forma à respeitar , se descobre o valor: com o qual se obtêm em MF: segundos. Então o novo .
Comandos no Matlab:
Note:
1) angulos3.m deve ser acompanhado da função: arc.m para poder funcionar!
2) Para usar angulos3.m já deve estar disponível a avariável G (uma tf que corresponde a transfer fucntion da planta: ) no ambiente de trabalho do Matab (Workspace):
>> help angulos3 programa para Projeto de Lead atrav��s de contribui����o angulas Fernando Passold, em 23/11/2019, revisado em 30/05/2020 Baseado em "example_9_4.m" de /UCV/Control/ (2009) Lead Compensator Desing (NISE) Exige como entrada (para funcionar), as seguintes vari��veis: G=tf( , ) Gera texto na tela compat��vel com Markdown>>Caso se interesse você pode tentar entender o código usando:
>> edit angulos3.mNote: se você tentar executar angulos3.m sem existir a variável G, teremos um erro:
>> angulos3## Lead Controller DesignIn this version you should arbitrate the initial position of the ZERO of C(z)Plant (in s-plane) informed, G(s):```matlab Undefined function or variable 'G'.Error in angulos3 (line 27)zpk(G) >>Então, iniciando este projeto, informando a planta, temos:
>> G = tf ( 1, poly( [0 -4 -6] ) )G = 1 ------------------- s^3 + 10 s^2 + 24 s Continuous-time transfer function.>> zpk(G) 1 ------------- s (s+6) (s+4) Continuous-time zero/pole/gain model.>> angulos3O que gera:
Lead Controller Design
In this version you should arbitrate the initial position of the ZERO of C(z)
Plant (in s-plane) informed, G(s):
ans = 1 ------------- s (s+6) (s+4) Continuous-time zero/pole/gain model.Maximum overshoot desired (%OS), in %: ? 30
The damping factor should be:
Enter desired settling time, : ? 1.3
It results in the natural oscillation frequency, (rad/s)
The MF poles (in the s-plane) should be located in:
Enter the position of the controller ZERO (): ? -4
C_aux = s + 4 Continuous-time transfer function. Angular contribution of each pole in the s-plane:
Sum of angular contribution of poles,
Angular contribution of each zero in the s-plane:
Sum of angular contribution of zeros,
Final angle for the pole of ,
Final position for the Lead pole:
The Lead controller final result is (variable C_Lead):
ans = (s+4) --------- (s+480.5) Continuous-time zero/pole/gain model.The (variable ftma_Lead):
ans = (s+4) ----------------------- s (s+480.5) (s+6) (s+4) Continuous-time zero/pole/gain model.Final RL graph:
Fim do script, Favor observar janelas gráficas...
Ajeitando os gráficos gerados:
xxxxxxxxxx>> figure(1); axis([-10 1 -1 9]) % No gráfico mostrando contribuições angulares| Gráfico sem zoom: | Gráfico ajustado (zona de interesse): |
|---|---|
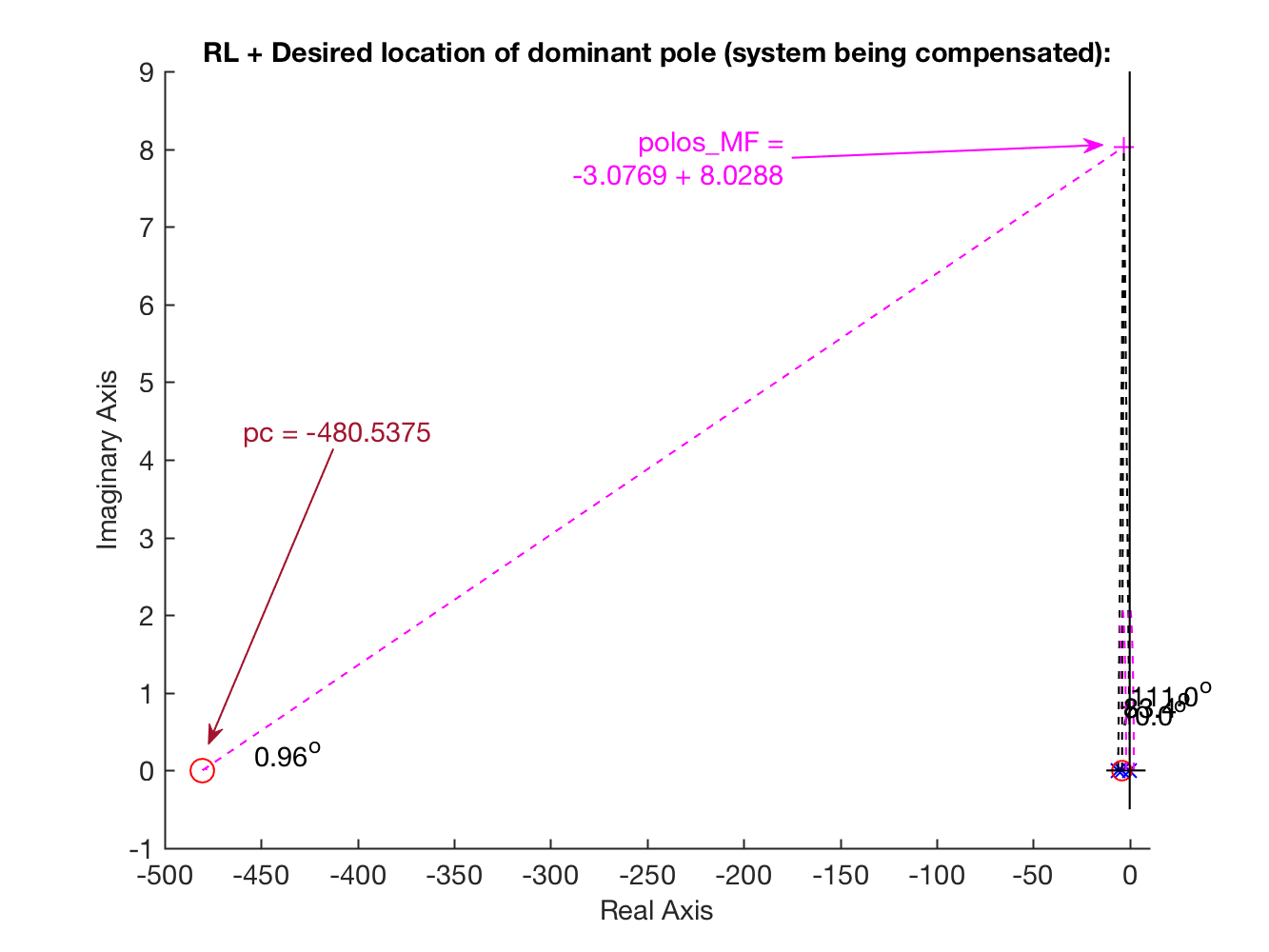 |  |
Note que com o ajuste anterior, não se percebe o pólo deste controlador defindo em (bastante distante dos outros pólos e zeros da ).
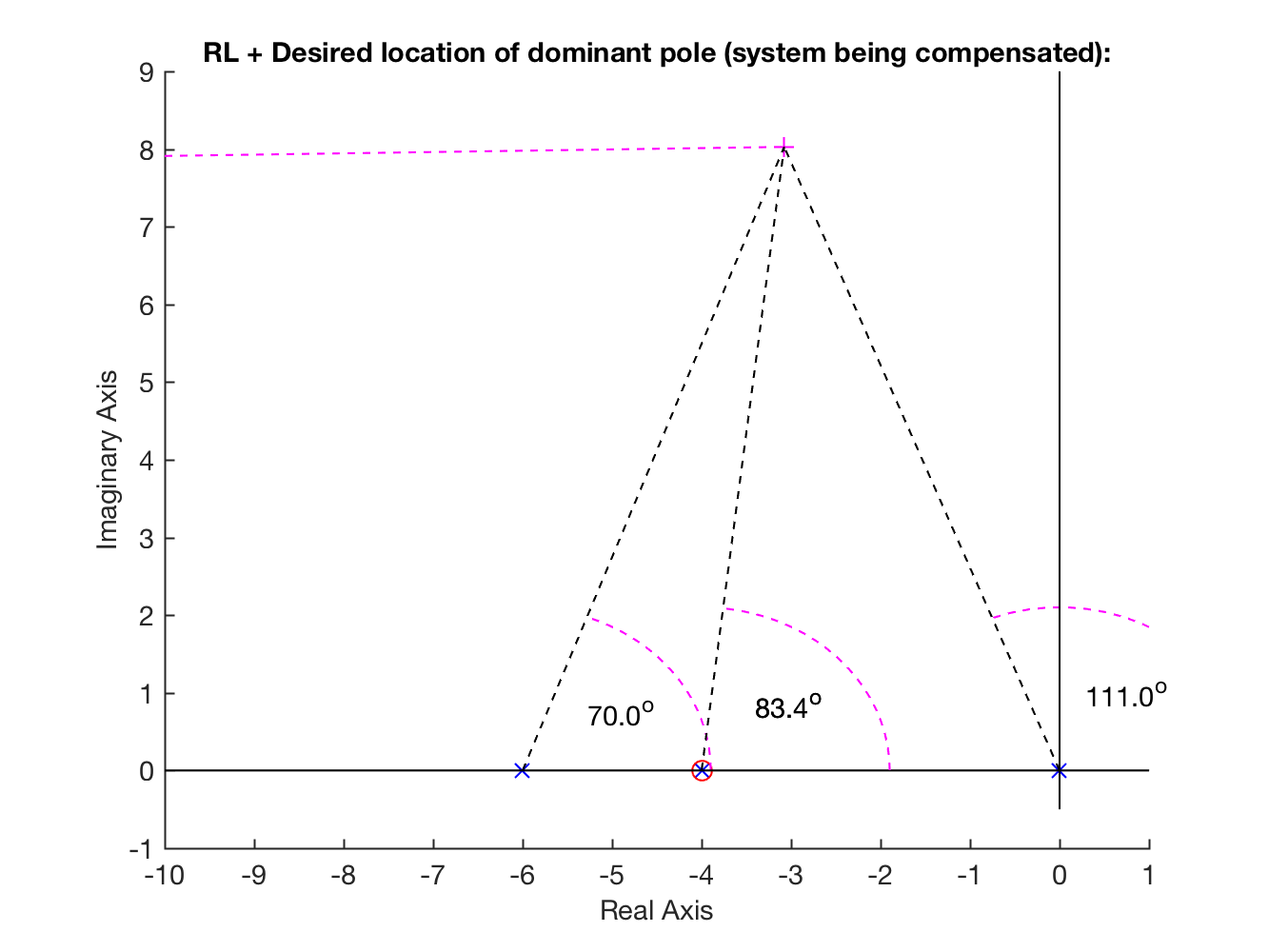
Ajustando a segunda janela gráfica (já com o RL da incluindo eq. completa do Lead):
xxxxxxxxxx>> axis([-10 1 -9 9])resulta em:
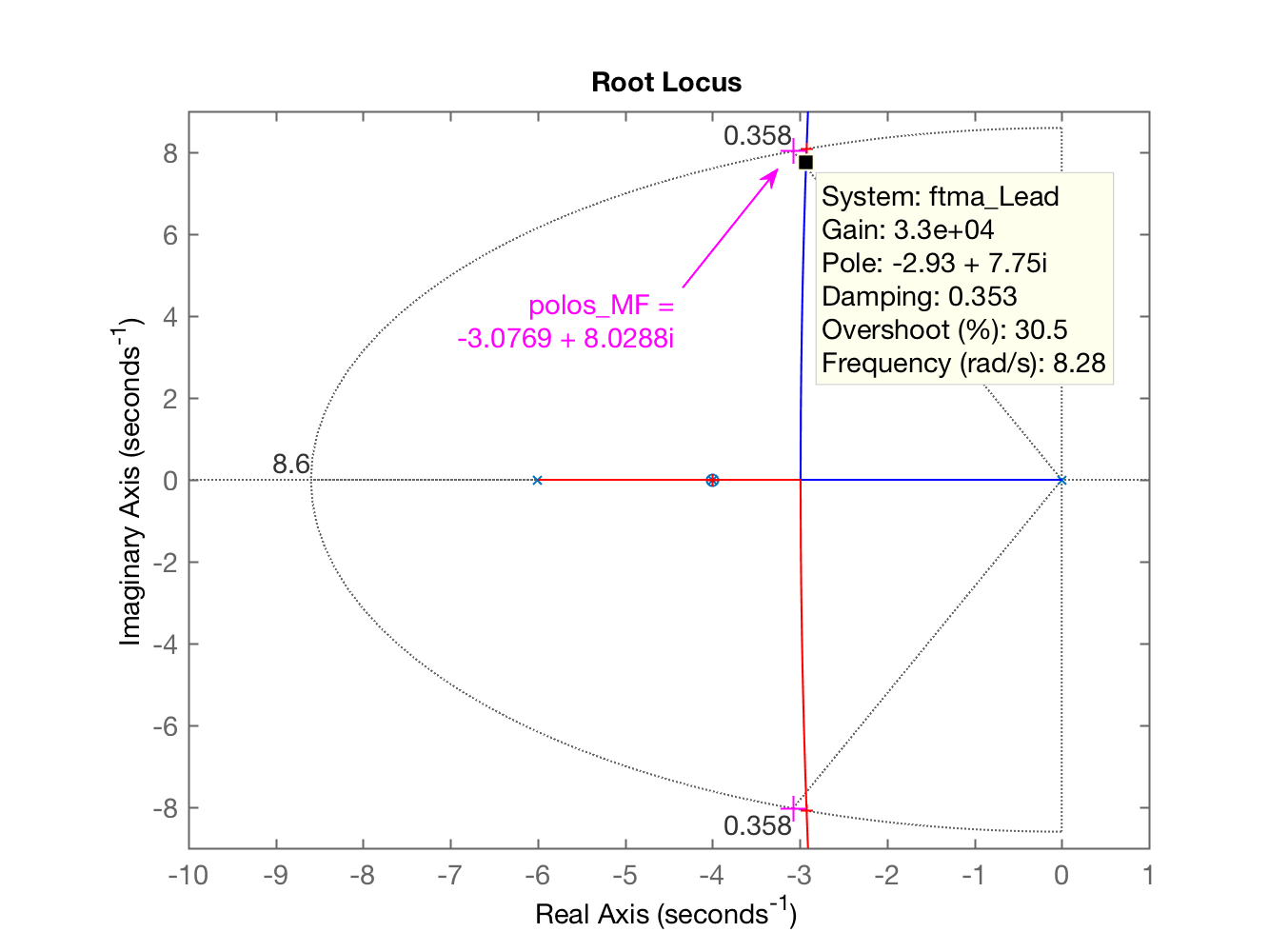
Continuando com o projeto iniciado por angulos3.m (note que este script não determina o ganho necessário para o controlador, apenas termina com o gráfico do RL pronto para definição do ganho do mesmo):
xxxxxxxxxx>> [K_Lead, polosMF] = rlocfind (ftma_Lead)Select a point in the graphics windowselected_point = -2.9230 + 8.0805iK_Lead = 3.5491e+04polosMF = 1.0e+02 * -4.8069 + 0.0000i -0.0292 + 0.0808i -0.0292 - 0.0808i -0.0400 + 0.0000i>> % fechando a malha>> ftmf_Lead = feedback(K_Lead*ftma_Lead, 1);>> figure; step(ftmf_Lead)>> ftmf_Lead2 = feedback(32000*ftma_Lead, 1); % ajustando ganho para reduzir algo o %OS>> figure; step(ftmf_Lead, ftmf_Lead2)>> legend('Lead (K=35.491)', 'Lead (K=32.000)')E temos então 2 gráficos:
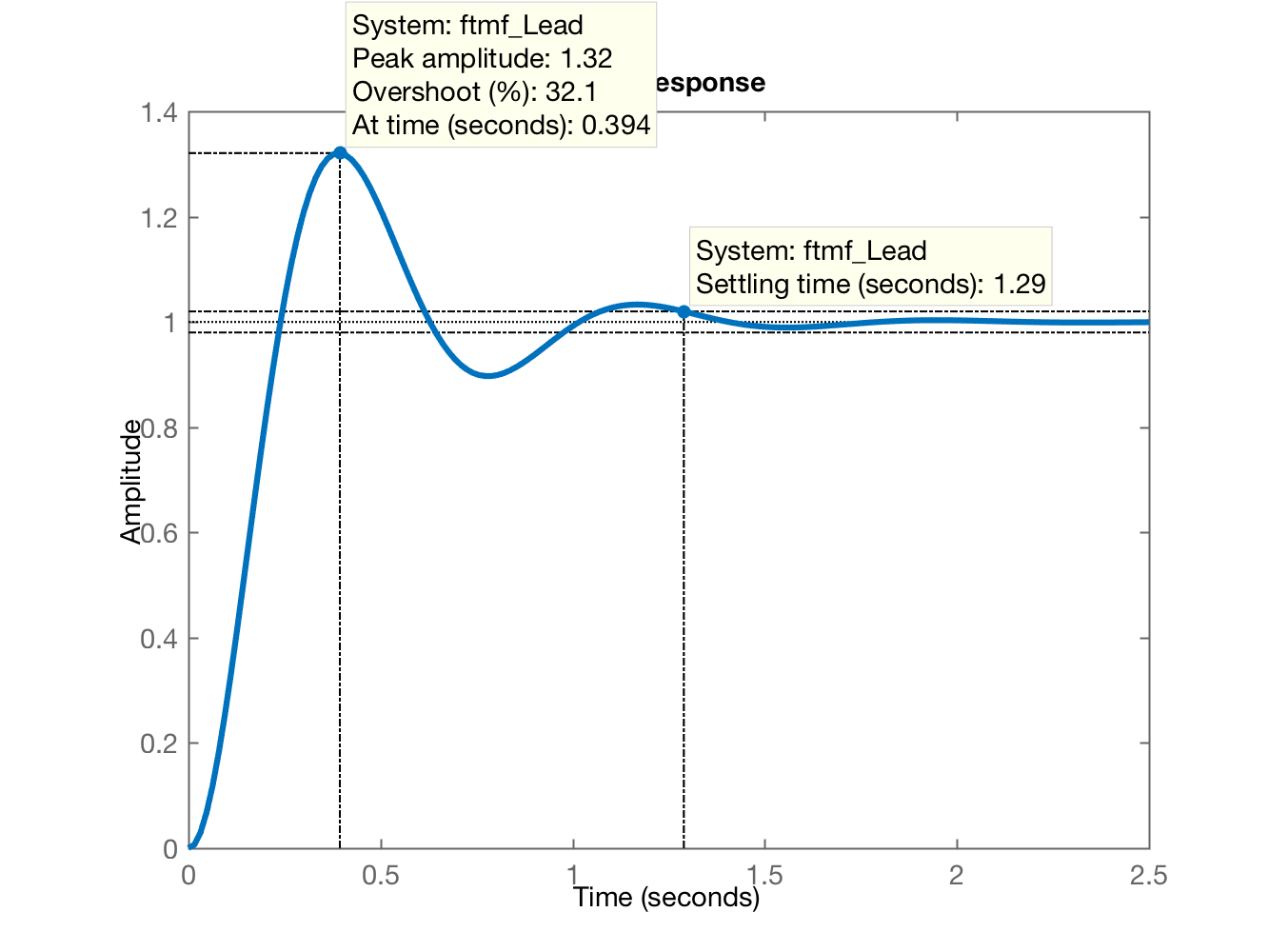
E o gráfico que compara com o mesmo Lead mas com ganho reduzido para , de forma a manter o :
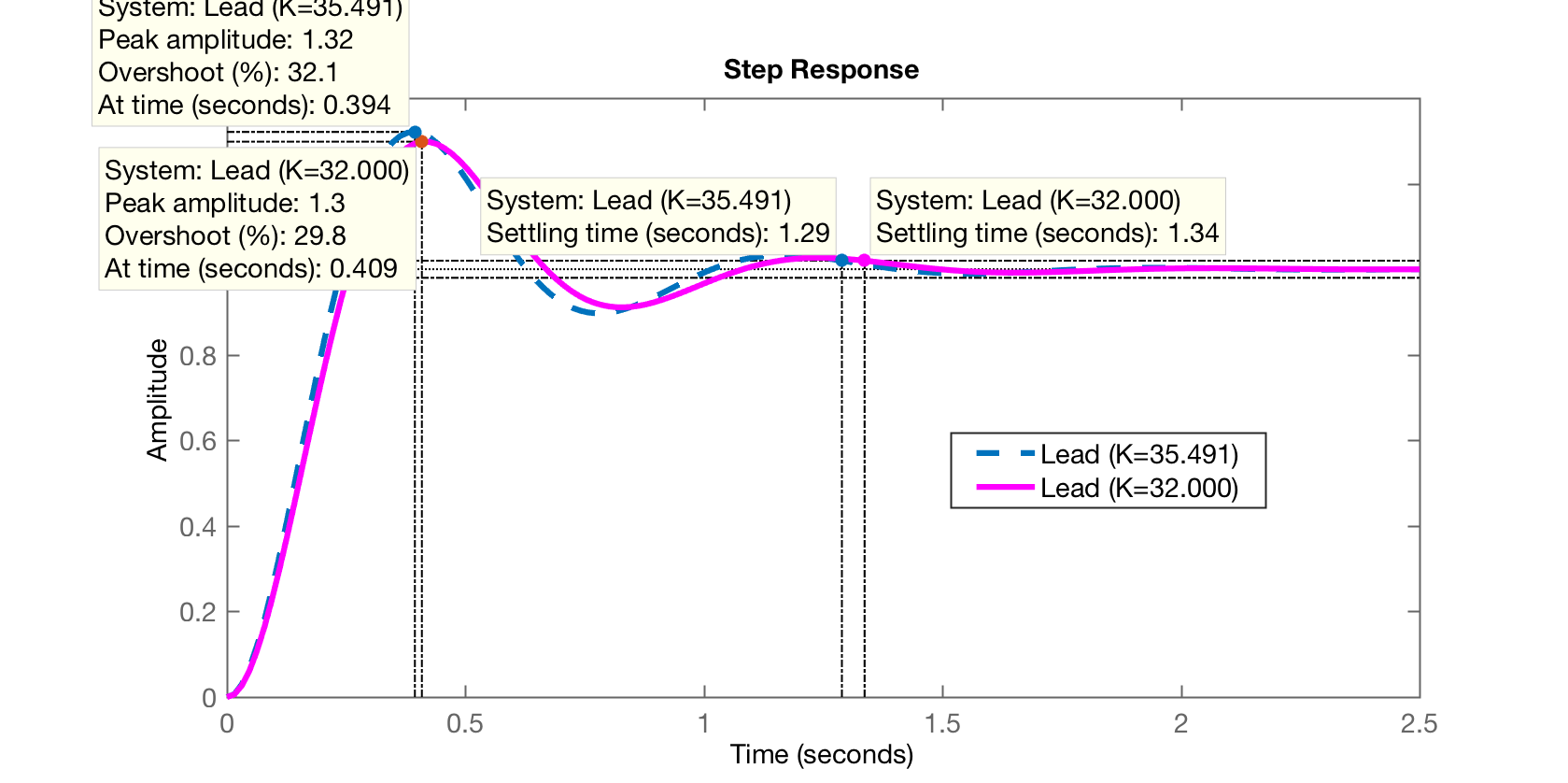
Fim.
Fernando Passold, em 09.06.2021